Seismic Shift Meaning
The Earth is in a constant state of change. Earth’s crust, called the lithosphere, consists of 15 to 20 moving tectonic plates. The plates can be thought of like pieces of a cracked shell that rest on the hot, molten rock of Earth’s mantle and fit snugly against one another. The heat from radioactive processes within the planet’s interior causes the plates to move, sometimes toward and sometimes away from each other. This movement is called plate motion, or tectonic shift.
Our planet looks very different from the way it did 250 million years ago, when there was only one continent, called Pangaea, and one ocean, called Panthalassa. As Earth’s mantle heated and cooled over many millennia, the outer crust broke up and commenced the plate motion that continues today.
Seismic Meaning
The huge continent eventually broke apart, creating new and ever-changing land masses and oceans. Have you ever noticed how the east coast of South America looks like it would fit neatly into the west coast of Africa? That’s because it did, millions of years before tectonic shift separated the two great continents.
Earth’s land masses move toward and away from each other at an average rate of about 0.6 inch a year. That’s about the rate that human toenails grow! Some regions, such as coastal California, move quite fast in geological terms — almost two inches a year — relative to the more stable interior of the continental United States. At the “seams” where tectonic plates come in contact, the crustal rocks may grind violently against each other, causing earthquakes and volcano eruptions. The relatively fast movement of the tectonic plates under California explains the frequent earthquakes that occur there.
Seismic shift synonyms and antonyms in the English synonyms dictionary, see also 'schismatic',schismatical',sadistic',septic', definition. Understand seismic shift meaning. ‘Cramer believes that US broadcasting underwent a seismic shift on September 11 last year.’ Origin Mid 19th century from Greek seismos ‘earthquake’ (from seien ‘to shake’) + -ic. Seismic shift definition is - a great change. How to use seismic shift in a sentence.
Seismic is about acoustic vibration. The archetypal oscillation, the sine wave, describes the displacement y of a point around a circle. You only need three pieces of information to describe it perfectly: the size of the circle, the speed at which it rotates around the circle, and where it starts from expressed as an angle. These quantities are better known as the amplitude, frequency, and phase respectively. These figures show how varying each of them affects the waveform:
So phase describes the starting point as an angle, but notice that this manifests itself as an apparent lateral shift in the waveform. For seismic data, this means a time shift. More on this later.
What about seismic?
We know seismic signals are not so simple — they are not repetitive oscillations — so why do the words amplitude, frequency and phase show up so often? Aren't these words horribly inadequate?
Not exactly. Fourier's methods allow us to construct (and deconstruct) more complicated signals by adding up a series of sine waves, as long as we get the amplitude, frequency and phase values right for each one of them. The tricky part, and where much of where the confusion lies, is that even though you can place your finger on any point along a seismic trace and read off a value for amplitude, you can't do that for frequency or phase. The information for those are only unlocked through spectroscopy.
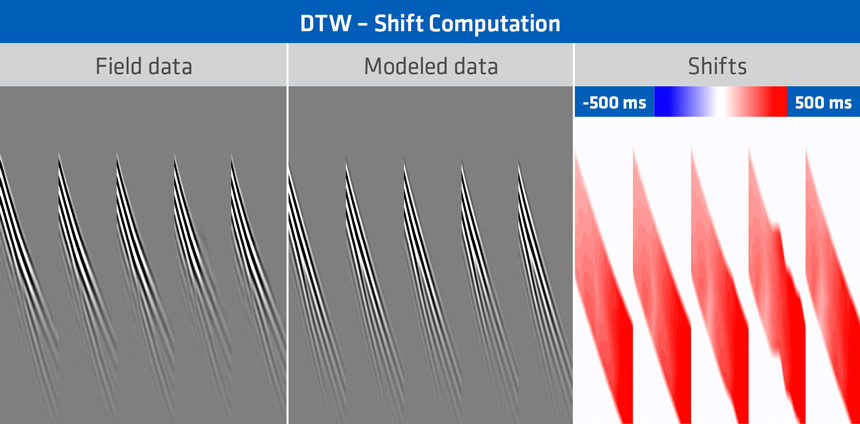
Phase shifts or time shifts?
The Ricker wavelet is popular because it can easily be written analytically, and it is comprised of a considerable number of sinusoids of varying amplitudes and frequencies. We might refer to a '20 Hz Ricker wavelet' but really it contains a range of frequencies. The blue curve shows the wavelet with phase = 0°, the purple curve shows the wavelet with a phase shift of π/3 = 60° (across all frequencies). Notice how the frequency content remains unchanged.
So for a seismic reflection event (below), phase takes on a new meaning. It expresses a time offset between the reflection and the maximum value on the waveform. When the amplitude maximum is centered at the reflecting point, it is equally shaped on either side — we call this zero phase. Notice how variations in the phase of the event alter the relative position of the peak and sidelobes. The maximum amplitude of the event at 90° is only about 80% of the amplitude at zero phase. This is why I like to plot traces along with their envelope (the grey lines). The envelope contains all possible phase rotations. Any event whose maximum value does not align with the maximum on the envelope is not zero phase.


Understanding the role of phase in time series analysis is crucial for both data processors aiming to create reliable data, and interpreters who operate under the assertion that subtle variations in waveform shape can be attributed to underlying geology. Waveform classification is a powerful attribute... but how reliable is it?
In a future post, I will cover the concept of instantaneous phase on maps and sections, and some other practical interpretation tips. If you have any of your own, share them in the comments.
See also
External links
Seismic Shift Meaning Wikipedia
| find literature about seismic phase |
Meaning Shift
- P is for Phase — blog post at Agile
Additional reading
Liner, C (2002). Phase, phase, phase. The Leading Edge 21, p 456–7. Abstract online.
Seismic Shift Meaning Art
